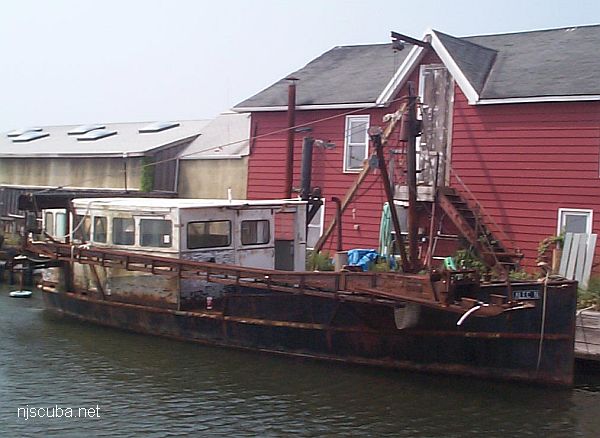
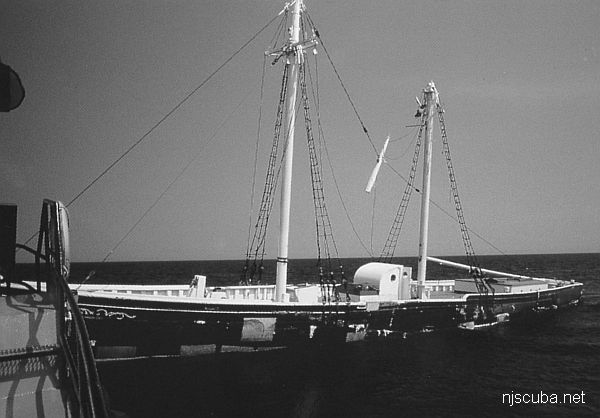
- Type:
- artificial reef, tanker
- Built:
- 1940, John H. Mathis, Camden NJ USA
- Specs:
- ( 247 x 38 ft )
- Sponsor:
- Spentonbush Red Star Company, Fisherman Magazine
- Sunk:
- Tuesday June 10, 1986 - Garden State North Artificial Reef
- GPS:
- 39°37.727' -74°01.079'
- Depth:
- 85 ft
More: AH Dumont YO-54 ...

- Type:
- artificial reef, tugboat
- Built:
- 1939, Southern Shipbuilding, Slidell LA as Rowen Card
- Specs:
- ( 106 x 26 ft ) 263 tons
- Sponsor:
- Ann E Clark Foundation
- Sunk:
- Thursday Sept 25, 2003 - Deepwater Artificial Reef
- GPS:
- 39°58.004' -74°10.721'
More: AJ McAllister YNT-12 ...

- Type:
- artificial reef, tanker, US Navy, YO-20 class
- Built:
- 1918, Todd Shipyards, New York NY USA, as YO-31
- Specs:
- ( 161 x 25 ft ) 335 tons light, 911 tons full-load
- Sponsor:
- Crystal Oil Corporation, Marine Trades Assn. of NJ, Fisherman Magazine
- Sunk:
- Thursday September 10, 1987 - Sea Girt Artificial Reef
- GPS:
- 40°06.440' -73°41.130'
- Depth:
- 125 ft
More: Alan Martin YO-31 ...