Marine Shellfish

These animals are lumped together here because they all have hard external shells. Crustaceans and Mollusks are not closely related at all. This is more of a restaurant classification than a scientific one.
- American Lobster
- Crabs ...
- Other Crustaceans ...
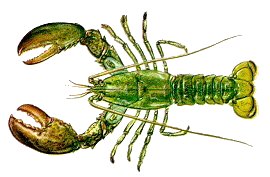
Homarus americanus
Size: to 36" and 45 lbs. (record)
Habitat: subtidal to the edge of the continental shelf, in any sheltered spot
Notes:
Lobsters differ from shrimps in having three pairs of clawed legs, the first with very large claws. Southern "Spiny Lobsters" are only distantly related; freshwater crayfish are closer. Lobsters, or "Bugs", are mainly nocturnal, and feed primarily on living or freshly killed food rather than scavenging on carrion, as was once thought. Although they are predominantly solitary creatures, lobsters do have a sort of social life amongst themselves. Males are more aggressive than females and will form pecking orders among individuals in an area. Female lobsters apparently seek the protection of a male when molting, then mate afterward. Lobsters shed their shells once or twice a year, depending mainly on the temperature.
More: American Lobster ...
These are all so-called "true crabs".
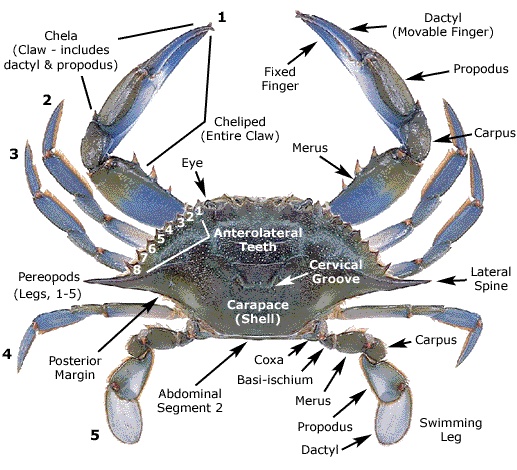
True crabs are crustaceans with extremely reduced tails, which are carried folded under the body. Males are generally larger than females. Presented here are just the most common of many local species. Sizes quoted below are body width. Hermit Crabs are listed elsewhere. They are not closely related.
More: Crabs ...
Here is an assortment of miscellaneous crustaceans, just a tiny sample of the incredible diversity of this group. Barnacles are also crustaceans, however, because of their alternative lifestyle I have decided to include them elsewhere.
More: Other Crustaceans ...
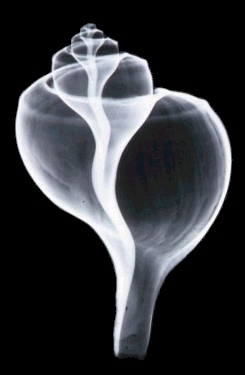
These creatures are all of the order Gastropoda - having a single, often coiled, shell, as opposed to the bivalves, which have two matching shells. Most snails are hermaphroditic. Also, most snails have a right-hand twist to the shell, although there are exceptions.
Right:
X-ray image of a Channeled Whelk, showing internal structure.
Nudibranchs are a form of snail that has lost its shell, while Corollas and Sea Butterflies are snails that have abandoned not just their shells, but the snail-like existence entirely, swimming up into the water column as plankton.
More: Snails ...
All of these bivalves are filter feeders. The other major group of mollusks is the Gastropods or snails. Squid and octopus ( cephalopods ) are mollusks too, but they don't behave like other mollusks, so I included them elsewhere. Teredos are bivalves that have evolved a worm-like wood-boring habit.
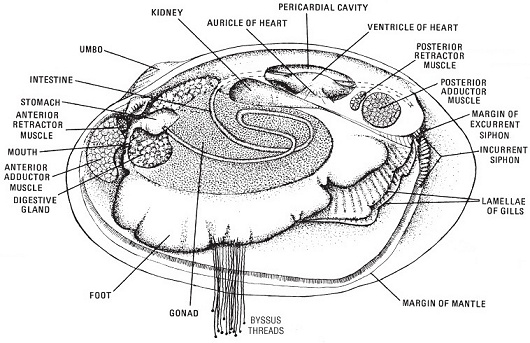
More: Bivalves ...

by Kathy Johnston
Courtesy of Jacques Cousteau National Estuarine Research Reserve
- Home ...
- Dive Sites ...
- Artificial Reefs ...
- Marine Biology ...
- Artifacts ...
- Gear & Training ...
- Blog ...
- Cozumel ...
More: Marine Biology & Ecology ...

