Search for: Mohawk (2/6)

What I know about antique glass bottles wouldn't cover both sides of a matchbook. But here are some excellent links on the subject, so you too can learn the difference between a pontil and a blob:
Miscellaneous Links:
Right: Plastic Coke bottle with screw top
More: Bottles ...
A tugboat is a small sturdy and powerful vessel designed to push or tow other vessels and barges

You will see them in every sizable port; smart, businesslike small ships, low in the water and surging out to a large inbound ship. Tugs represent power for pushing and pulling, an engine with just enough hull for adequate buoyancy. Thick fenders for close-quarters work, pushing a big ship alongside the quay against the wind, hauling her off at the end of a towing wire.
More: Tugboat ...

A liner is a vessel designed primarily to carry passengers on a set schedule. There was a time when ocean liners were more than the mere pleasure cruisers of today. Before the advent of modern air travel, ships were the primary means of transport for those needing to cross the oceans. Untold numbers of immigrants came to this country in passenger liners, most in steerage class, a far cry from the modern floating pleasure palaces.
More: Liner ...
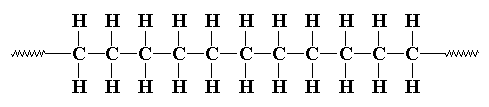
Polymer materials - rubbers, plastics, and silicones - are not really of interest as artifacts. They are, however, among the most important materials to divers: without neoprene, nylon, and a bewildering range of other polymer materials, we would not have most of the equipment that makes diving possible!
More: Polymer Materials ...
Rock is an aggregation of solid matter composed of one or more of the minerals forming the earth's crust. The scientific study of rocks is called petrology. Rocks are commonly divided, according to their origin, into three major classes - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
Not all rock-like materials are created by nature. Almost all civilizations have depended to some extent on artificial building materials, the most common of which are concrete, brick, and asphalt.
More: Rock & Stone ...

Glass is a hard substance, usually brittle and transparent, composed chiefly of silicates and an alkali fused at high temperature.
Composition and Properties of Glass
Most glass is a mixture of silica obtained from beds of fine sand or from pulverized sandstone; an alkali to lower the melting point, usually a form of soda or, for finer glass, potash; lime as a stabilizer; and cullet ( waste glass ) to assist in melting the mixture. The properties of glass are varied by adding other substances, commonly in the form of oxides, e.g., lead, for brilliance and weight; boron, for thermal and electrical resistance; barium, to increase the refractive index, as in optical glass; cerium, to absorb infrared rays; metallic oxides, to impart color; and manganese, for decolorizing.
More: Glass & Ceramics ...

Copper, brass, and bronze are all relatively immune to saltwater corrosion. Brass artifacts of all sorts are easily cleaned up into shiny souvenirs for those who value them. Bright green copper sheets and tubes add color to many wrecks, while bronze is the material of choice for the most coveted of all diver's artifacts - a ship's bell.
Copper and some of its alloys have been used by humanity since the Bronze Age. One of the first metals known to humans, free copper was probably mined in the Tigris-Euphrates valley as long ago as the 5th century BC. Cyprus, from which the metal's name originally comes, was the primary source of copper in the ancient world.
More: Copper, Brass & Bronze ...
LOST AT SEA:
A treatise on the management and ownership
of shipwrecks and shipwreck artifacts
by Michael C. Barnette

Somewhere out on the ocean, a ship is in distress. Tossed about by churning seas and brutal winds, the vessel struggles to stay afloat. Her crew puts forth a valiant effort while passengers, many incapacitated by waves of nausea spawned by the ever-moving deck underneath their feet, huddle together in fear. The hull is slowly breached, and seawater steadily invades the ship. As the blitzkrieg of flooding water rises to extinguish the boiler fires, the vessel loses all power. Cast in darkness and overwhelmed by the noise of the howling wind and crashing surf, the sea tears off sections of the crippled ship, carrying away numerous unfortunate souls. The end is near.
More: Maritime Salvage Law ...
Finding a Shipwreck
by Capt. Steve Nagiewicz

Of course, finding a shipwreck is a necessary prerequisite for finding artifacts. Many wreck locations are well known. Others are secrets, and many wrecks have yet to be discovered. While you can recover artifacts from almost any shipwreck, it is these "virgin" wrecks that are often the best producers of prize items like portholes, deadeyes, and china. But how do you find a wreck like this? Research is the most productive method. This will require visiting local libraries, historical societies, nautical museums, and many other institutions. It means lots of reading and digging for information. Be prepared to spend some time searching for clues that aren't willing to be found.
More: All About Artifacts ...

