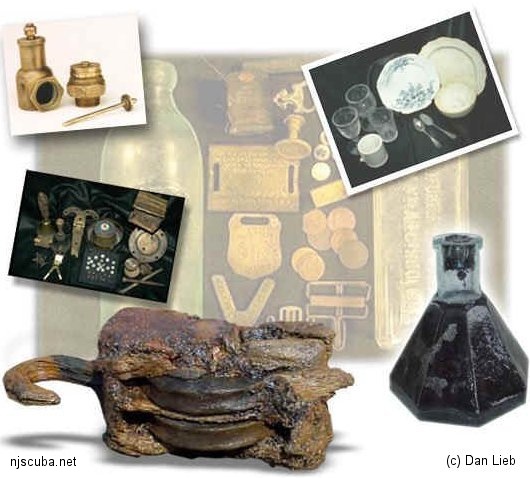
Shipwrecks

More: Bits & Cleats ...
Anchors

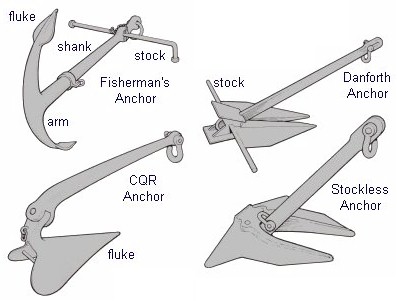
Not all artifacts are easily recoverable. Ship's anchors often weigh in the hundreds or thousands of pounds and require a well-planned expedition to bring back to shore. At right is an assortment of anchors, from the old-fashioned "Fisherman's" anchor of the 1800s to the modern stockless or "naval" anchor, and its small cousin, the Danforth anchor.
More: Anchors & Chain ...
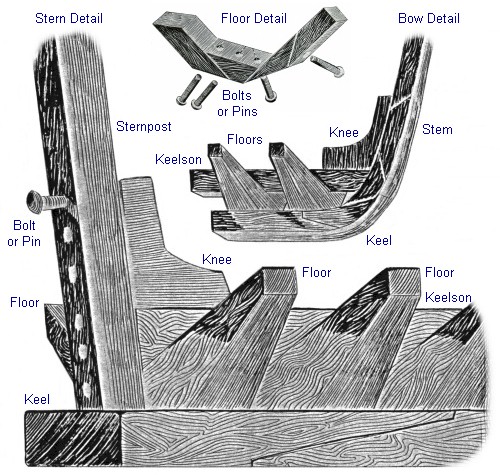
Wooden ships have been constructed for thousands of years. Around the world, many different construction techniques have been used, some of them quite extraordinary. The ancient Greeks stitched the planks of their warships together edgewise to form an extremely light frameless load-bearing shell, much like a modern airplane fuselage. However, most wooden ships are built using a basic framing system that has changed little over the centuries.
More: Wooden Ship Construction ...


Possibly the most preposterous artifact that has ever been recovered is one of the masts from the Lightship Relief. Over 50 ft long and weighing some 6000 pounds, the mast was recovered by divers in 1976 and set up in front of a dive shop in Laurence Harbor. ( It was called "Diver's Cove". )
The dive shop has long since closed, and the huge mast now lies off to the side, a rusting eyesore. The present owner of the property claims it is a registered historic landmark. Apparently not so - as of March 2008 it was hauled away as garbage. Better that it had just been left in the sea, but this is the fate of many divers' "artifacts."
More: Masts ...
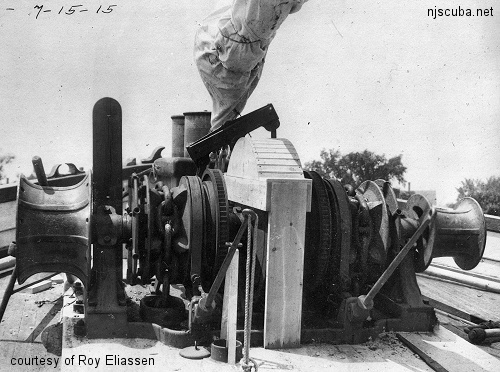
Prior to steam power, the only force available on a sailing ship to perform all the necessary work was the men on board. For some tasks, such as raising the anchor, it might be necessary to yoke the entire crew to a multi-deck manual capstan. On the largest vessels, even with every available man, this might take several hours to complete. With the advent of steam power, a "donkey engine" and a single engineer could do the work of many men, in less time, and these were soon installed in almost all vessels.
More: Capstans & Winches ...
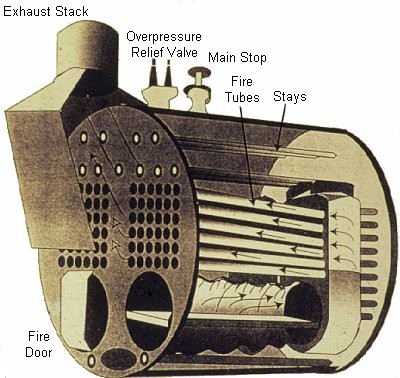
Boilers are one of the most common shipwreck features, found on almost all engine-powered vessels. The purpose of a boiler is to produce high-pressure steam for the engine to propel the vessel. Steam boilers have been in use from the early 1800s to the present day.
More: Boilers ...


