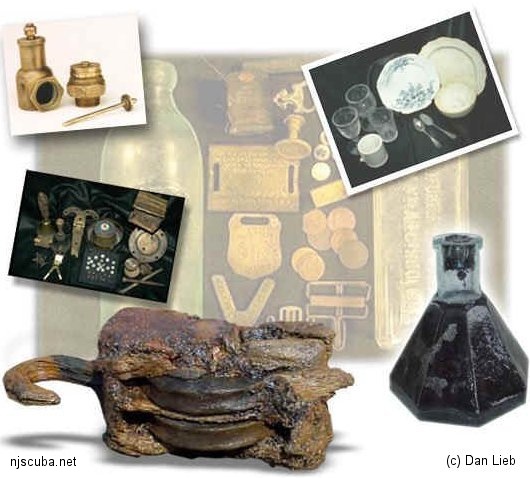
Miscellaneous
Port & Starboard
port - the left side of a ship, when facing forward
starboard - the right side of a ship, when facing forward
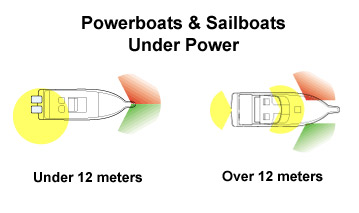
The starboard side of a vessel ( or an airplane ) carries a green running light, and the port side carries a red running light. The best way to remember all this is: port, left and red are all short words, while starboard, right, and green are all long(er) words.
More: Glossary of Terms ...
I find this sort of material to be much more interesting than the endless rehashing of coral reefs, glowingly useless gear reviews, and "buoyancy tips" that fill up the standard glossy diving magazines.
Historical
Conservation Manual – Donny L. Hamilton

The Oxford Companion to Ships and the Sea
Peter Kemp, 1988
Lots of interesting information and trivia.
More: Artifacts References ...
Marine distance measurements are expressed in terms of nautical miles. A nautical mile is significantly different from a common or statute mile. The conversion is 1 nautical mile = 1.151 statute miles, or approximately 6076 ft ( vs. 5280 ft for a statute mile. )
Why such a confounded thing as this? Here's why:
More: Distance & Navigation ...
LOST AT SEA:
A treatise on the management and ownership
of shipwrecks and shipwreck artifacts
by Michael C. Barnette

Somewhere out on the ocean, a ship is in distress. Tossed about by churning seas and brutal winds, the vessel struggles to stay afloat. Her crew puts forth a valiant effort while passengers, many incapacitated by waves of nausea spawned by the ever-moving deck underneath their feet, huddle together in fear. The hull is slowly breached, and seawater steadily invades the ship. As the blitzkrieg of flooding water rises to extinguish the boiler fires, the vessel loses all power. Cast in darkness and overwhelmed by the noise of the howling wind and crashing surf, the sea tears off sections of the crippled ship, carrying away numerous unfortunate souls. The end is near.
More: Maritime Salvage Law ...

How do two ships in the wide ocean collide? It seems unlikely, and yet it happens all the time. Often, the ocean is not all that wide. Many collisions occur in shipping lanes and port approaches, where ships are brought together in close proximity. Here are some videos of actual collisions between ships:
More: Collision at Sea ...
Finding a Shipwreck
by Capt. Steve Nagiewicz

Of course, finding a shipwreck is a necessary prerequisite for finding artifacts. Many wreck locations are well known. Others are secrets, and many wrecks have yet to be discovered. While you can recover artifacts from almost any shipwreck, it is these "virgin" wrecks that are often the best producers of prize items like portholes, deadeyes, and china. But how do you find a wreck like this? Research is the most productive method. This will require visiting local libraries, historical societies, nautical museums, and many other institutions. It means lots of reading and digging for information. Be prepared to spend some time searching for clues that aren't willing to be found.
More: All About Artifacts ...