Schooner Barges (1/3)
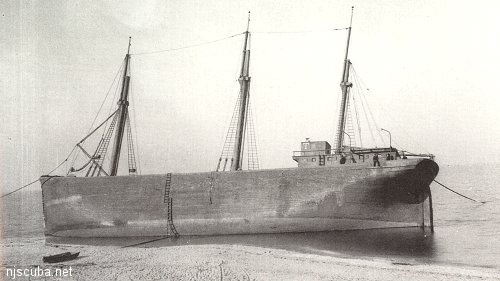
The schooner barge was the final development of the working sailing ship. The design originally evolved in the 1870s on the Great Lakes, where it was found that sailing ships could be more profitably towed from place to place than sailed. No longer subject to the vagaries of the wind, such trips could be made on a scheduled basis, and with reduced labor costs. The idea spread into general use, resulting in the conversion of many sailing ships into barges. Ironically, most of the vessels that were converted to schooner barges were not actually schooners, but square-rigged ships. Square-riggers, with their large and expensive crews of skilled sailors, became uneconomical to operate in the face of ever-improving steam power, while more efficient schooners managed to compete for a few years longer.
More: Schooner Barge ...

- Type:
- shipwreck, barge / schooner barge
- Specs:
- 1313 tons
- Sunk:
- Thursday January 26, 1933
four casualties - Depth:
- 75 ft
More: Anastasia ...
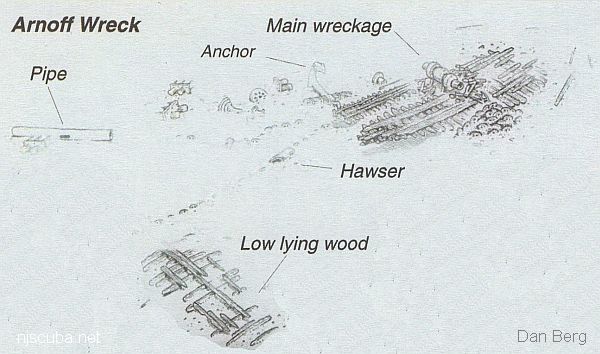
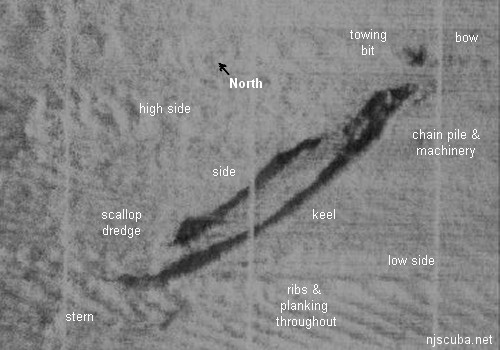
- Type:
- shipwreck, schooner barge
- Specs:
- ( 200 ft est.)
- Sunk:
- late 1800s ?
- Depth:
- 80 ft
More: Arnoff ...
- Type:
- shipwreck, schooner barge
- Specs:
- ( 330 x 40 ft )
- Sunk:
- March 12, 1932
- Depth:
- 95 ft
Capt. Mick Trzaska of the dive boat CRT II also calls this the "Bomb Wreck", since it once produced a live aircraft-type explosive. * A diver had sent it up with a lift bag thinking it was a champagne bottle! How it got there is anyone's guess.
* Probably a World War II hedgehog.
More: Asfalto ...
- Type:
- shipwreck, schooner barge
- Built:
- 1922, Baltimore MD USA as John H Winstead
- Specs:
- ( 215 x 36 ft ) 1160 tons
- Sunk:
- Monday December 5, 1927
foundered in storm - no casualties - Depth:
- 80 ft
More: Cadet - John H. Winstead ...

- Type:
- shipwreck, schooner barge ( originally a bark )
- Built:
- 1876 as Parknook
- Specs:
- ( 199 x 32 ft ) 793 tons
- Sunk:
- Saturday September 12, 1931
foundered - GPS:
- 40°25.374' -73°52.828' (AWOIS 2013)
- Depth:
- 60 ft
More: Cecilia M. Dunlap ...
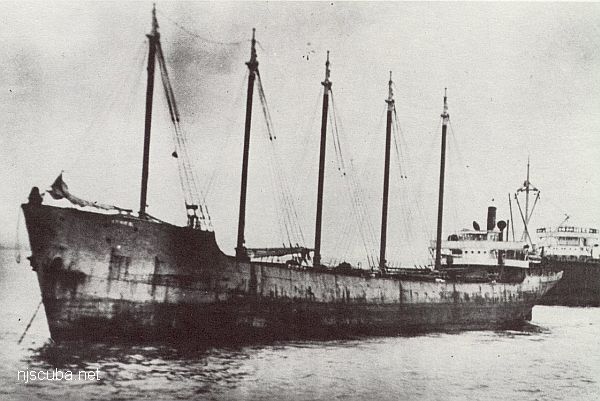
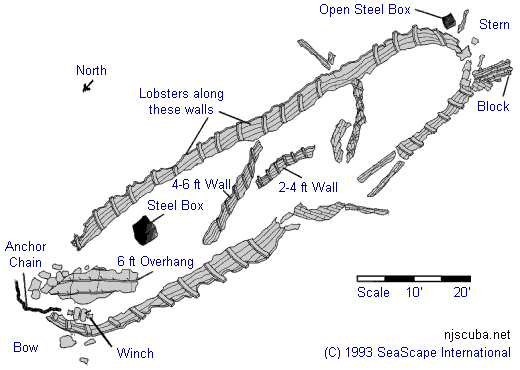
- Type:
- artificial reef, schooner barge, USA
( The small smokestack in the pictures is for an electrical generator. ) - Built:
- 1919, Union Shipbuilding, Baltimore MD USA
- Specs:
- ( 306 x 35 ft ) 2072 tons, 14 crew
- Sponsor:
- Modern Transportation Co.
- Sunk:
- July 1983 - Sea Girt Artificial Reef
- GPS:
- 40°06.964' -73°57.571'
- Depth:
- 65 ft
More: Dykes ...
- Type:
- shipwreck, schooner barge
- Depth:
- 80 ft
Another schooner barge or sailing ship. Close to shore and very near the Maurice Tracy. It is sometimes a second or third dive because of this. She's in 70 feet of water on a sandy seafloor. Lots of wood walls and some decking, it's been better for spearfishing lately rather than bugs, but that'll depend on when she was last dived. Named after the fishing boat that found the spot.
More: Gassoon ...
- Type:
- shipwreck, schooner barge
- Depth:
- 75 ft
A typical smallish schooner barge wreck of unknown origin. Some anchor chain and decking spread out over a small area, with a few smaller pieces way off the main piece. Named after the fishing boat that found the spot.
More: Glory Wreck ...

- Type:
- shipwreck, schooner barge(s)
- Sunk:
- late 1800s
- Depth:
- 80 ft
More: Hankins Wrecks ...