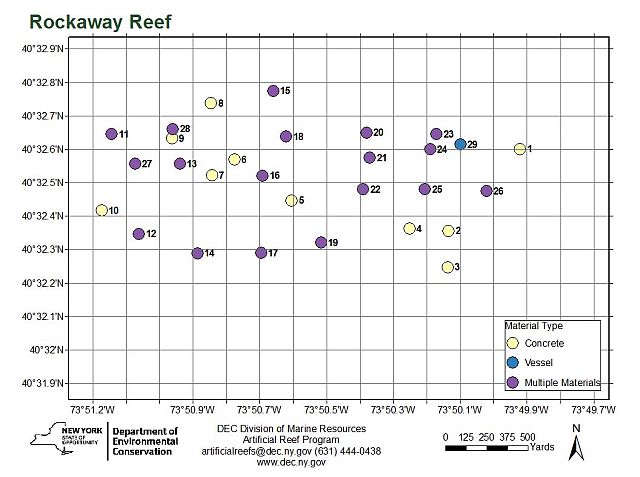
Rockaway Artificial Reef
Rockaway Artificial Reef
1.6 nautical miles south of Rockaway Beach, 1.00 sq miles
Depth: 32 - 40 ft
Not Shown:
- 60 steel buoys
- 2,000 tire units
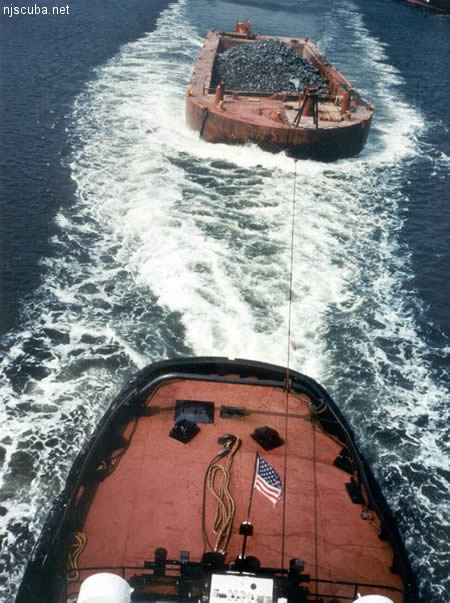


All manner of concrete, steel, and stone rubble from dredging, demolition projects, and other construction is used as artificial reef materials. This material is generally available at very low cost or free from construction companies who are more than happy to get rid of it. Transportation costs determine where this material is used by the Reef Program.
More: Rock & Rubble ...

It must cost a fortune to rent this giant derrick.
- Type:
- artificial reef, barges
- Depth:
- 32 - 40 ft
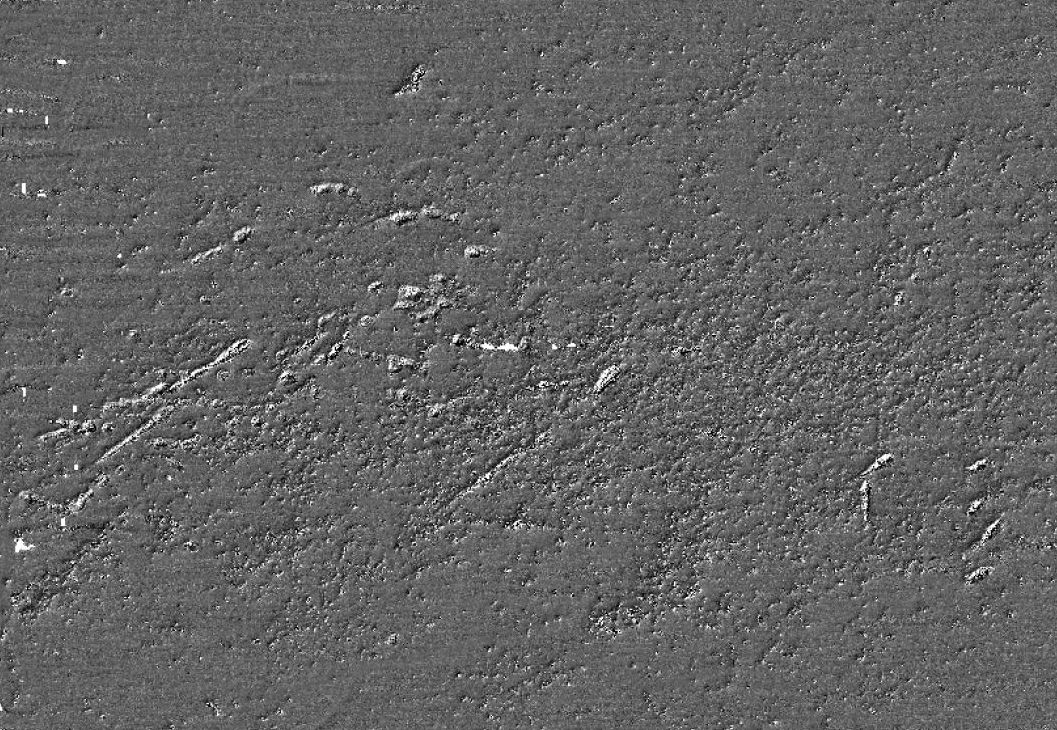
| Name | Description | Sunk | GPS |
| Dump Scow DS-109 |
100 ft steel | Tuesday Oct 9, 2018 |
40°32.614' -73°50.098' |
More: barges - Rockaway Artificial Reef ...
Artificial Reef Charts, Charts, Dive Sites, Long Island West Dive Sites, New York Artificial Reef Charts, New York Dive Sites, Sandy Hook Dive Sites,
Sandy Hook / Rockaway Inlet Chart
- Barge #10
- 3 Sisters
- Ambrose Buoy
- A Street - Shark River
- Acara
- Across
- Ajace
- Allenhurst Jetty
- Arnoff
- Arundo
- Asfalto
- Aurora
- Ayuruoca
- BA Wreck
- Shark River - Back Bay
- Balaena
- Bald Eagle
- BD1738
- USS Benson
- Beth Dee Bob
- Blue Boy
- Bronx Queen
- Bug Light
- Charles Dunlap
- Cecilia M Dunlap
- Chauncy Jerome
- Cornelia Soule
- Choapa
- coal (Lido)
- Continent
- crane barge
- Daghestan
- Dragger
- drydock
- Dryland
- Edwin Duke / Stone Barge
- dump
- Edmund Phinney
- East Rockaway Inlet
- Ed's Schooner
- Elberon Rocks
- Eureka
- Finance
- Fort Victoria
- German
- GL78
- Glen II
- I.P. Goulandris
- Gypsy
- Horseshoe Cove
- Alexander Hamilton
- Happy Days
- Howard
- Iberia
- Immaculata
- Inshore Schooner
- Jack I
- Jones Inlet
- Jones Tug
- Klondike Rocks
- Larsen
- Lizzie D
- Long Branch locomotives
- H.W. Long
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Margaret
- Mistletoe
- R.C. Mohawk
- Nautilus
- Navesink River
- Northeast Sailor
- New Reef
- New Deal
- New Era
- HMS Pentland Firth
- Long Branch Pier Rubble
- Pinta
- Pipe Barge
- Pliny
- Plymouth
- Pocopson
- Princess Anne
- Ruth Shaw
- Robert A Snow
- Ramos
- Ranger
- Relief Lightship
- Rickseckers
- Rjukan
- Rockaway Inlet
- Rockaway Belle
- Roda
- Rudder Wreck - Pocono
- Rusland / Adonis
- Scotland Buoy
- Sandy Hook Pilot Boat
- SC-60
- Shark River Inlet
- Shrewsbury Rocks
- Spring Lake Sailor
- Steel Wreck
- Stolt Dagali
- Sylvanus
- Tampa III
- USS Turner
- AWOIS 8087
- AWOIS 8097
- u11
- AWOIS 7509
- AWOIS 7932
- AWOIS 9768
- AWOIS 12966/11422
- AWOIS 1609
- AWOIS 8084
- AWOIS 7940
- AWOIS 7938
- AWOIS 8076
- AWOIS 4600
- AWOIS 8075
- Valerie E
- Vega
- Warrior
- Edward W Winslow
- Edward W Winslow
More: Long Island West Dive Sites Chart ...
Sandy Hook / Rockaway Inlet Chart
- Barge #10
- 120 Wreck
- 3 Sisters
- Ambrose Buoy
- A Street - Shark River
- Acara
- Across
- Adele
- Ajace
- Alex Mac
- Allenhurst Jetty
- Antioch
- Arnoff
- Arundo
- Asfalto
- Aurora
- Ayuruoca
- BA Wreck
- Shark River - Back Bay
- Balaena
- Bald Eagle
- BD1738
- USS Benson
- Beth Dee Bob
- Blue Boy
- Bronx Queen
- Bug Light
- Charles Dunlap
- Cecilia M Dunlap
- Catherine Jackson
- Chauncy Jerome
- Cornelia Soule
- Choapa
- coal (Lido)
- Continent
- crane barge
- Daghestan
- Dragger
- drydock
- Dryland
- Edwin Duke / Stone Barge
- dump
- Dutch Springs
- Edmund Phinney
- East Rockaway Inlet
- Ed's Schooner
- Elberon Rocks
- Eureka
- Finance
- Fort Victoria
- German
- GL78
- Glen II
- I.P. Goulandris
- Gypsy
- Horseshoe Cove
- Alexander Hamilton
- Howard
- Iberia
- Immaculata
- Inshore Schooner
- Jack I
- Joan La Rie III
- Jones Inlet
- Jones Tug
- Klondike Rocks
- Larsen
- Lizzie D
- Long Branch locomotives
- Logwood
- H.W. Long
- Macedonia
- Mahogany
- Malta
- Manasquan Inlet
- Margaret
- Marion
- Mistletoe
- R.C. Mohawk
- Manasquan Wreck
- Nautilus
- Navesink River
- Northeast Sailor
- New Reef
- New Deal
- New Era
- HMS Pentland Firth
- Long Branch Pier Rubble
- Pinta
- Pipe Barge
- Pliny
- Plymouth
- Pocopson
- Princess Anne
- Ruth Shaw
- Robert A Snow
- Ramos
- Ranger
- Relief Lightship
- Rickseckers
- Rjukan
- Rockaway Inlet
- Rockaway Belle
- Round Valley
- Roy's barge
- Rudder Wreck - Pocono
- Rusland / Adonis
- Scotland Buoy
- Sandy Hook Pilot Boat
- SC-60
- Sea Girt Inlet
- Sea Girt Wreck
- Shark River Inlet
- Shrewsbury Rocks
- Spring Lake Sailor
- Steel Wreck
- Stolt Dagali
- Sylvanus
- Tampa III
- USS Turner
- AWOIS 8087
- AWOIS 8097
- u11
- AWOIS 7509
- AWOIS 7932
- AWOIS 9768
- AWOIS 12966/11422
- AWOIS 1609
- AWOIS 8084
- AWOIS 7940
- AWOIS 7938
- AWOIS 8076
- AWOIS 4600
- AWOIS 8075
- Valerie E
- Vega
- Warrior
- Delaware River Water Gap
- Western World
- Edward W Winslow
- Edward W Winslow
More: Sandy Hook Dive Sites Chart ...