Pelagics
The only trait that these fishes share is that they are all found in the open ocean.
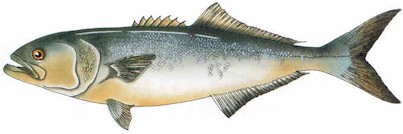
Pomatomus saltatrix
profile by John McClain, Principal Fisheries Biologist
Range:
The Bluefish occurs in temperate and warm waters of the western Atlantic from Nova Scotia to Uruguay, off the West African shelf, in the Mediterranean and Black Seas, in the Indian Ocean, and off Tasmania and Australia. In the United States, there are two major fishing areas, Cape Cod Bay to Cape Lookout and Cape Canaveral to Pompano Beach.
More: Bluefish ...
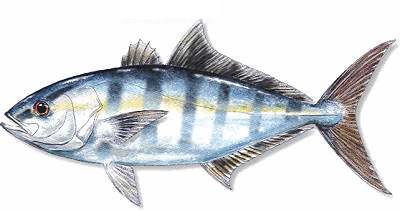
Seriola zonata
Size
to 24"
Habitat
Coastal surface waters, congregating around any floating objects
Description
Juveniles ( shown, up to 12" ) are attractively patterned with six or seven dark bars; these are lost in adults, which are also much slimmer. Schools of small Rudderfish can often be found around boats, and even around divers hanging on the anchor line. Pilotfish are similar, but larger and retain dark bars throughout life.
More: Banded Rudderfish ...

Peprilus tricanthus
Size
to 12"
Habitat
Coastal waters.
Baby Butterfish are often found sheltering in the tentacles of stinging jellyfishes, to which they are not immune. One slip and they're dead!
More: Butterfish ...

Scomber scombrus
Size
to 22" and 7 lbs.
Description
The Atlantic Mackerel is typically an open ocean fish with voracious feeding habits. They travel in schools that often contain thousands of fish. The swift swimming mackerel has a streamlined body and swims at high speeds for extended periods of time searching for food. All individuals within a specific school tend to be the same size. Since cruising speed increases significantly with age and size, scientists believe that conformity of body size within a specific school is necessary to allow all fish to maintain identical swimming speeds. Mackerel may grow as large as 7-1/2 pounds and have a maximum age of about 20 years.
More: Atlantic Mackerel ...

by Bruce Freeman
Six of the world's 13 tuna species occur off New Jersey each year. Among the most beautiful and powerful of sea creatures, the tops of their heads and their upper backs are either solid or wavy lines of dark, lustrous, metallic blue. Their sides are silver or silver-gray, often with silvery spots, bands, and iridescent hues of purple, pink and gold and silvery-white on the belly. Most young tunas have striking vertical bars along the body flanks, although these disappear with age. The beautiful coloration and patterns serve as camouflage.
More: Tunas ...

Seriola dumerili
Size
to 60" and 175 lbs. in the tropics
Description
The coloration of the greater amberjack is characterized by a dark stripe on the head which extends from the origin of the first dorsal gin through the eye. The back is blue or olivaceous, and the sides and belly are silvery-white. Occasionally there is an amber or pinkish cast to the body. Juveniles have five or six dark vertical bars along the sides.
More: Greater Amberjack ...
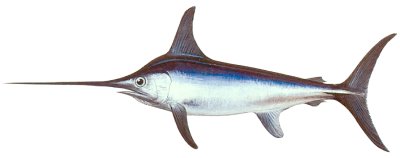
Xiphias gladius
Profile by Bill Figley
Fisheries Biologist
Range and Habitat:
Swordfish are found in temperate and tropical waters. On the East Coast, they extend from the Caribbean to Newfoundland. They occur in New Jersey waters almost year-round but are most abundant from July to October. Swordfish are pelagic, occurring in the open ocean in depths of over 300 fathoms. They prefer waters 55-65°F. During the summer they concentrate along the edge of the continental shelf but move further offshore to the warm Gulf Stream during the winter. Although swordfish are often seen basking on the surface, they spend most of their time deep in the water column.
More: Broadbill Swordfish ...

Lopholatilus chamaeleonticeps
Size: to 42" and 50 lbs.
Habitat
Deep waters around offshore canyons
These strange deep-sea fishes are found in the walls of the offshore canyons, far below the range of scuba divers, although they are caught by deep-sea fishermen. Their population is extremely cyclical, with large die-offs from excessively warm water, and this precludes any long-term commercial fishery.
More: Northern Tilefish ...
- Sea Basses & Porgies ...
- Blackfish & Cunner ...
- Cods & Allies ...
- Triggers, Puffers, & Sunfish ...
- Flounders ...
- Drums ...
- Ocean Bottom ...
- Baitfishes ...
- River & Inlet ...
- Pelagics ...
- Tropical Fishes ...
- Sharks - Inshore ...
- Sharks - Offshore ...
- Sharks - Dogfishes ...
- Skates & Rays ...
More: Marine Fishes ...
Fish

New Jersey now requires registration for saltwater fishing, including lobsters. Registration is free and can be done online at nj.gov/dep/saltwaterregistry.
This listing is for New Jersey waters only - if you cross into New York or Delaware, or Federal waters ( more than 3 miles offshore, ) you are subject to their regulations. Federal regulations supersede state regulations whenever stricter.
Lobster
More: Fishing Regulations ...

