San Saba
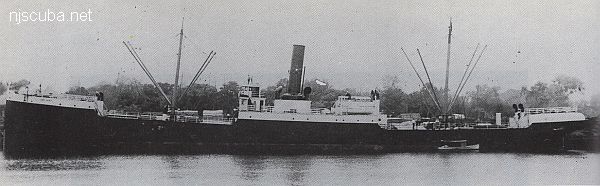
- Type:
- shipwreck, steamer, USA
- Name:
- San Saba is a river in central Texas, a tributary of the Colorado River of Texas.
- Built:
- 1879, Delaware River Iron Shipbuilding & Engine Works, Chester PA USA, as Colorado
- Specs:
- ( 306 x 39 ft ) 2458 gross tons, 37 crew
- Sunk:
- Friday October 4, 1918
struck mine laid by U-117 - 30 casualties - Depth:
- 80 ft
Being a hazard to navigation, the iron-hulled San Saba was demolished a week after sinking. Today she sits in 80 feet of water in two mangled pieces of wreckage. The bow section is a jumble of hull plates, with winches and other machinery still visible. The stern section, some 250 feet away is also broken up. The boilers are still visible at the end closest to the bow. Her propeller can still be found, as well as wreckage off to the starboard side. Many artifacts can still be found. Glassware, brass, .22 caliber bullets, and china are still being brought up with a little digging. The San Saba is sometimes called the "Southwest Barge", or the "Magnolia Wreck", for the anti-friction metal bars she was carrying.
A mine from the U-117 also sank the Chaparra.




Questions or Inquiries?
Just want to say Hello? Sign the .