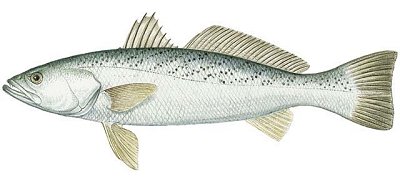
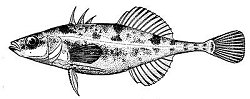
Drums
Drums are so named for their ability to make drumming sounds with their swim bladder. Actually, many fishes are capable of making sounds, from squeaks to growls, although not all Drums can "drum". Kingfish lack a swim bladder but still vocalize by grinding their pharyngeal (throat) teeth.