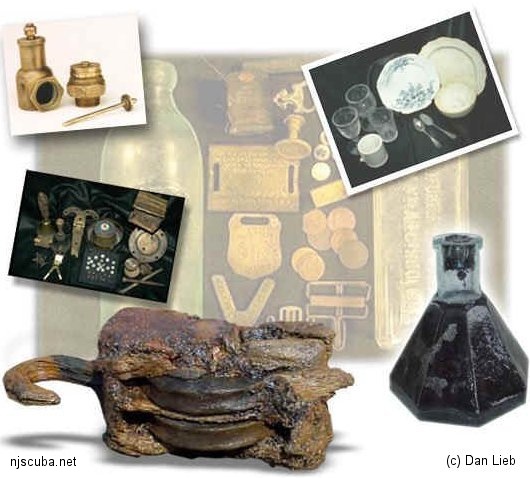
Miscellaneous
Another entry from the Way-back machine:


"Gentleman George"
by Dan Berg
Note: George Hoffman passed away January 14, 1997, about a year after this article was written. His death is a great loss to the diving community and he will be missed by us all.
More: Captain George Hoffman ...

How do two ships in the wide ocean collide? It seems unlikely, and yet it happens all the time. Often, the ocean is not all that wide. Many collisions occur in shipping lanes and port approaches, where ships are brought together in close proximity. Here are some videos of actual collisions between ships:
More: Collision at Sea ...
Side-scan sonar is a modern method of underwater imaging that can produce remarkably detailed and realistic views of shipwrecks and other bottom features using sound rather than light.
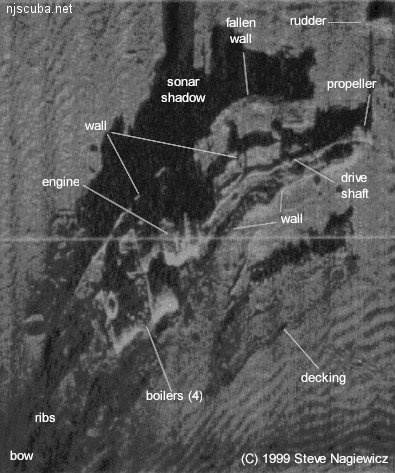
More: Side-scan Sonar ...

New Jersey scuba divers provide evidence of the identity of a popular New Jersey dive site
More: Identifying The Emerald ...

knife, the most tangible clue to the
identity of New Jersey's mystery U-boat.
In 1991, while checking out an obscure site known for hanging up fishing lines, I dropped down the anchor line only to find a virgin German U-boat. A wreck diver's fantasy of discovering a new shipwreck somehow had become a reality, and it was every bit as good as could be imagined. While reveling in the experience, I wondered if I would have enough skill and luck to ever make it happen again. Several discoveries later, the challenge is still irresistible.
More: Searching For Shipwrecks ...
Port & Starboard
port - the left side of a ship, when facing forward
starboard - the right side of a ship, when facing forward
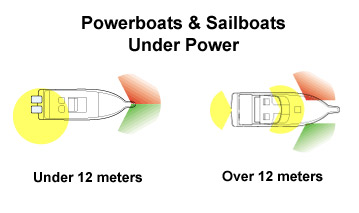
The starboard side of a vessel ( or an airplane ) carries a green running light, and the port side carries a red running light. The best way to remember all this is: port, left and red are all short words, while starboard, right, and green are all long(er) words.
More: Glossary of Terms ...


