Emerald - USS Hibiscus / Frances Wright (1/4)
- Type:
- shipwreck, steamer, USA
- Built:
- November 1864, S.M. Pook (see below), Fair Haven, CT
- Specs:
- 500 tons
- Sunk:
- Wednesday April 30, 1873
foundered after losing a propeller shaft - no casualties - Depth:
- 75 ft
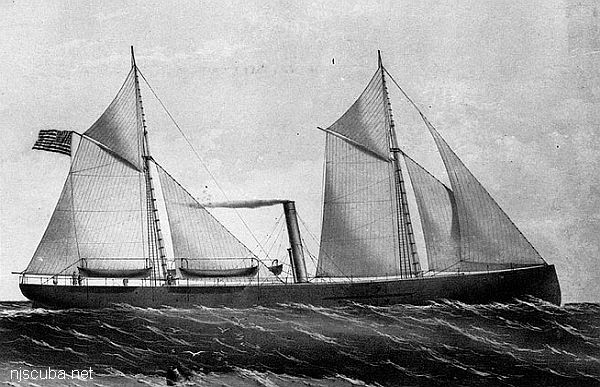
The "Emerald" wreck is probably the Hibiscus, a wood-hulled twin-screw steamer built in 1864 and commissioned into the U.S. Navy at that time. She saw service during the Civil War out of Tampa and Key West Florida. She was decommissioned in 1866 and sold in New York; later renamed Frances Wright, then renamed back to Hibiscus. While cruising off the New Jersey coast she broke a propeller shaft, took on water, and sank.
This is approximately what you'll find on the wreck site today: twin engines with part of one propeller shaft missing. The size of the wreckage also matches that of the Hibiscus. Capt. Steve adds: "We do a lot of digging here and find quite a bit of stuff, but nothing that actually names the wreck, although we've dated artifacts from 1872 and even found U.S. Navy emblems on personal effects." The redundant power plants also point to a Navy ship - this is an expensive configuration that would be unlikely on a commercial vessel.
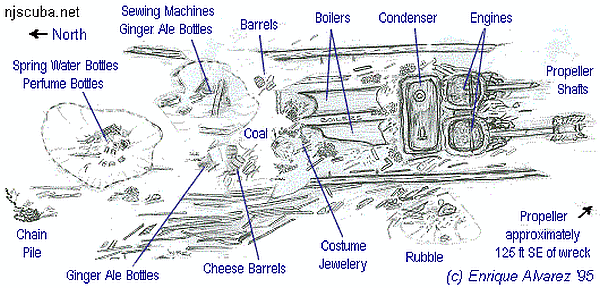
The Emerald is actually quite a small site to dive since most of the wreck lies buried beneath several feet of sand. The boilers are about as broken-down as boilers can be, but the unusual dual steam engines provide myriad nooks and holes for Sea Bass and other fish. If you tie off a reel and sweep out over the clean white sand, you can find the holes dug by artifact hunters, down to the blackened wood remains of the hull.




Questions or Inquiries?
Just want to say Hello? Sign the .