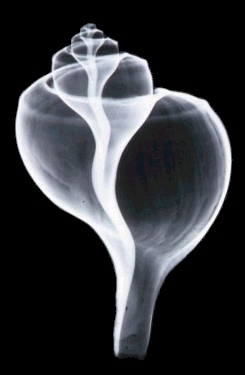
Northern Moon Snail
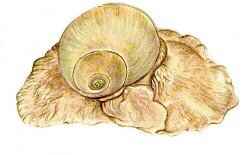
Lunatia heros
Size: to 4"
Habitat: generally in deeper water, but possible in shallows
Notes: quite common in places

These snails are responsible for the curious sand collars that divers often find. They produce a glue to cement the sand grains together into a protective ring for their eggs.
Moon Snails are predators of other shellfish, which they smother with their enormous foot. They are themselves sometimes eaten as Scungilli.