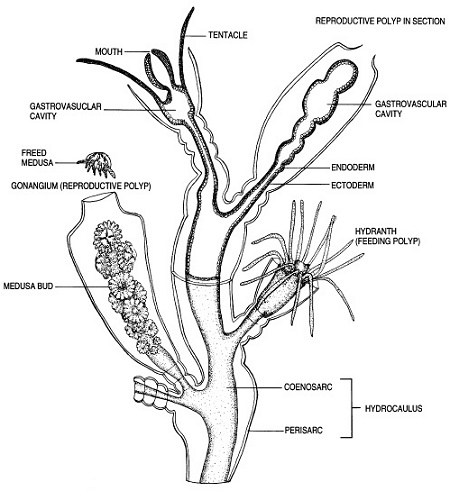
Hydroids
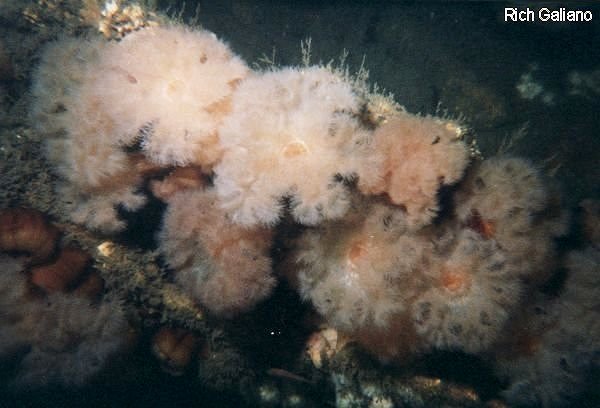
Masses of hydroids adorn many of the offshore wrecks, mixed in with anemones, sponges, mussels, coral, and algae. Hydroids are the most primitive Cnidarians, closely related to Hydromedusae, and display the most even split between the sessile polyp stages and free-swimming medusa stages, which are quite small and common.
The common Pink-Hearted Hydroid Tubularia spp generally grows in rounded tufts up to 6" across. Siphonophores are free-living hydroids that are often highly venomous, although most attached forms are harmless to humans.




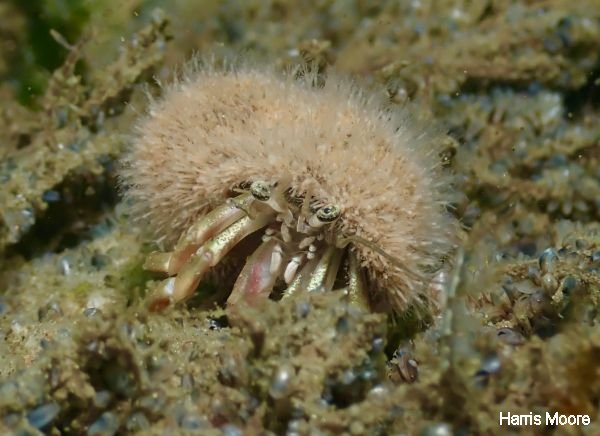
"Snail Fur" is a hydroid that grows as a pinkish fuzz only on shells inhabited by hermit crabs. Living snails that plow through the sand or empty shells that tumble with the waves and currents are not suitable homes for Snail Fur because of the abrasive action of the sand. But once the shell is commandeered by a hermit crab, most of its surface, except where the shell is dragged along behind the new homeowner and scrapes the sand, is kept out of the sediments and is available for colonization by the hydroids.