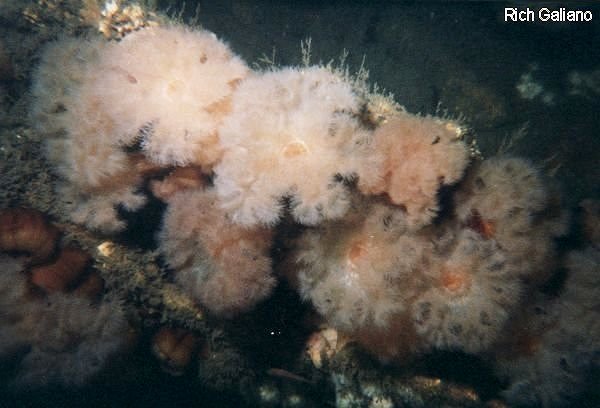
Sea Squirts

Molgula manhattensis ( right )
Styela Partita ( left )
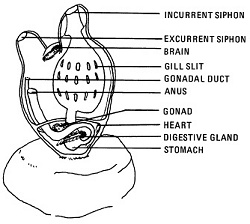
Sea Squirts are found attached intertidally to subtidally. They show an extraordinary tolerance for brackish and polluted water, which makes them highly survivable in urban areas. Sea Squirts, usually about an inch in diameter, are capable of ejecting a stream of water when agitated, hence the name. Usually found in groups of several animals. See also: Horned Salp.
Tunicates are much more advanced in the evolutionary scheme of things than anemones, having, for example, a circulatory system. The larvae actually even have several features in common with vertebrates, including the precursor of a spinal cord, but these are lost in the sac-like sessile adults.