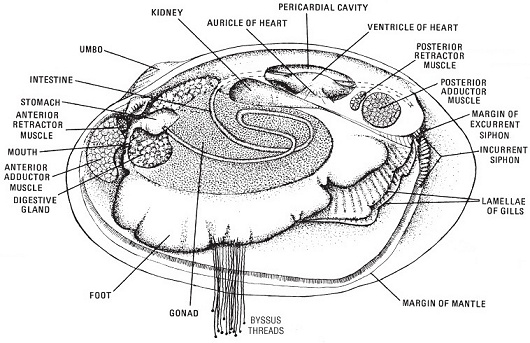
Oysters
The Common Oyster Crassostrea virginica, to 10", is the basis of a major fishery, but they occur only in turbid brackish estuaries, conditions generally not conducive to scuba diving. Oysters once dominated the bottom fauna in our local rivers and bays, but are now all but extinct due to pollution and disease. Attempts are being made to reintroduce them in places, and perhaps someday even re-establish the fishery. Disease-resistant Asian Oysters may be the key to this.