Starfish (Sea Star)

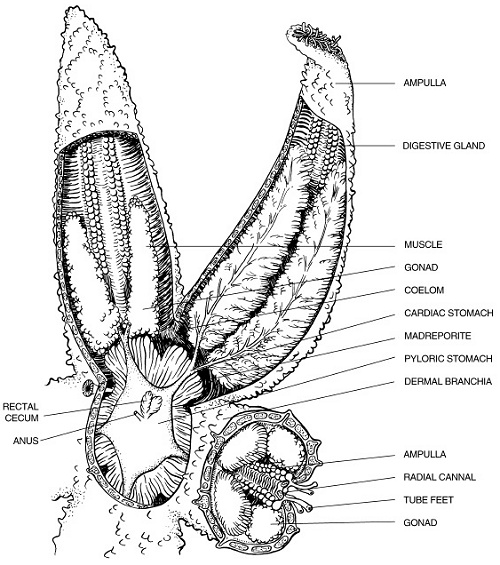
Starfish or Sea Stars are found on any solid structure, from inter-tidal rocks to deep wrecks. They are so common that one forgets just how bizarre they really are. These animals have 5-way body symmetry *, hydraulic tube feet, and ejects their stomach through their mouth to feed. ( Oddly, the planktonic larvae have bilateral symmetry, like higher animals. ) The "eye" is called a madreporite, and is actually the exhaust vent for the hydraulic system. They are capable of regenerating an entire animal from just a fragment. Starfish come in a rainbow of colors from yellow to lavender.

Forbes' Asterias ( above right ) are common in all environments from rivers to deep seas. The skin is covered with tiny spines, giving a rough texture. They grow to an arm length of 5 inches. Northern or Boreal Sea Stars Asterias vulgaris are generally similar to Forbeses, but rather larger ( arms to 8" ) and flabbier. They are more commonly found offshore. Blood Stars Henricia sanguinolenta ( right ) have a much smoother skin. They are found only in deeper waters offshore.
Brittle Stars Ophioderma spp ( below right ) have thin delicate arms that are very flexible and easily broken. They are capable of much

faster movements than other starfish, crawling, and in some cases even swimming. Brittle stars grow as large as 6 inches, but most are much smaller. They are usually found on muddy bottoms but may turn up anywhere.
Starfish often move so slowly that they don't seem to move at all. Large specimens from deep waters are surprisingly soft and soggy when you bring them up - collect small ones if you want souvenirs.
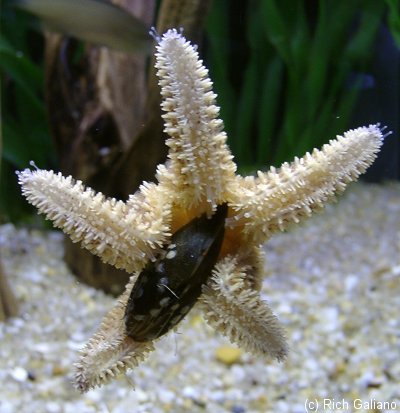





Contrary to the common conception of a drawn-out tug-of-war between the starfish and the mussel, the starfish does not pry open its victim by brute strength. Instead, the starfish inserts its stomach through whatever tiny gap or opening there may be between the shells of the bivalve, which it may widen only slightly by pulling. The digestive process then weakens the bivalve, eventually attacking the adductor muscles that hold the shell closed, and allowing the starfish to open it fully.
Peterson's states that starfish can "float free and drift on strong currents, " but the behavior you see here is not widely documented. These starfish are balled up and rolling in the surge. This appears to be a deliberate mode of transportation, quite a bit faster than they would otherwise travel. Video courtesy of Dan Crowell.
( The annoying tapping sound in the video is not the starfish - it is the boat's depth finder. )



