Tiger Shark

Galeocerdo cuvier
Size:
to 24 ft
Habitat:
open ocean, also enters rivers and bays at night
Notes:
extremely dangerous
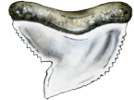
The serrated teeth are designed for sawing chunks from large prey items
If you are going to worry about a shark, let it be this one. Tiger Sharks are big, bold and inquisitive, and frequently come close inshore. They are also remarkably undiscriminating in their eating habits, which makes them even more likely to attack a swimmer, or anything for that matter.
Tiger sharks have the ability to evert ( turn inside-out ) their stomachs, much like starfish. This allows them to 'test' all sorts of food items that would otherwise choke them, like license plates and surfboards.





